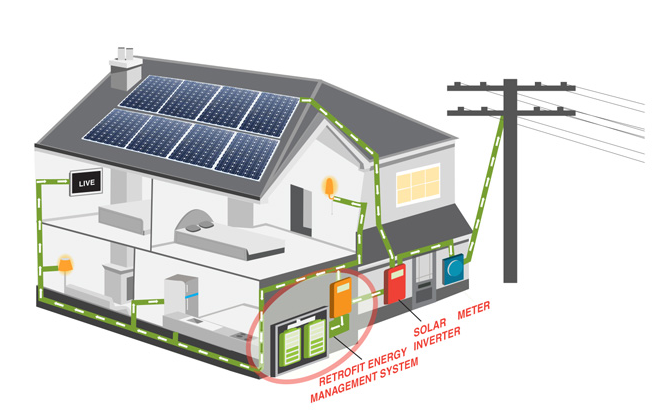
Everyone will be torn between buying a solar inverter or a hybrid inverter. Let’s go into the interesting realm of solar and hybrid inverters in this blog. The growing need for alternative energy sources necessitates understanding the significant differences between these two types of inverters.
Solar Inverter
Solar inverters are an important component of a solar power system. Their principal responsibility is to convert the direct current (DC) from the solar panels to alternating current (AC), which can then power buildings, business facilities, and other electrical appliances. Solar inverters are critical in maximizing the effectiveness of solar energy and ensuring its efficient use.
Here are some key properties and characteristics of solar inverters:
Changing from DC to AC:
Solar panels generate direct current (DC). However, the majority of electrical appliances and the power grid use alternating current (AC). The critical conversion is performed by solar inverters, which transform captured DC power into AC power that can be used immediately.
MPPT Technology:
Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) technology is included in many solar inverters. MPPT technology optimizes solar panel energy output by continually tracking and changing voltage and current to optimal efficiency. This ensures that, even under changing weather circumstances, the inverter functions at the maximum power point of the solar modules.
Monitoring and analysis:
Many current solar inverters include built-in monitoring systems that enable customers to track system performance and energy output as well as resolve any issues. Some inverters can communicate with web platforms or mobile apps, which provide real-time data and insights into energy output and consumption.
Longevity and efficiency:
Solar inverters have high efficiency ratings, often ranging from 95% to 98%. This means that they can convert a significant portion of the gathered solar energy into useful power. Inverters are also subjected to rigorous testing to ensure their longevity and dependability in a variety of environmental situations, such as high temperatures and humidity.

When selecting an inverter for your solar power system, consider your energy usage patterns, grid reliability, and budget. If you live in a location with regular power outages or consume a lot of energy, investing in a hybrid inverter with energy storage can be a good idea. However, if grid stability is not an issue, a solar inverter may be more cost effective.
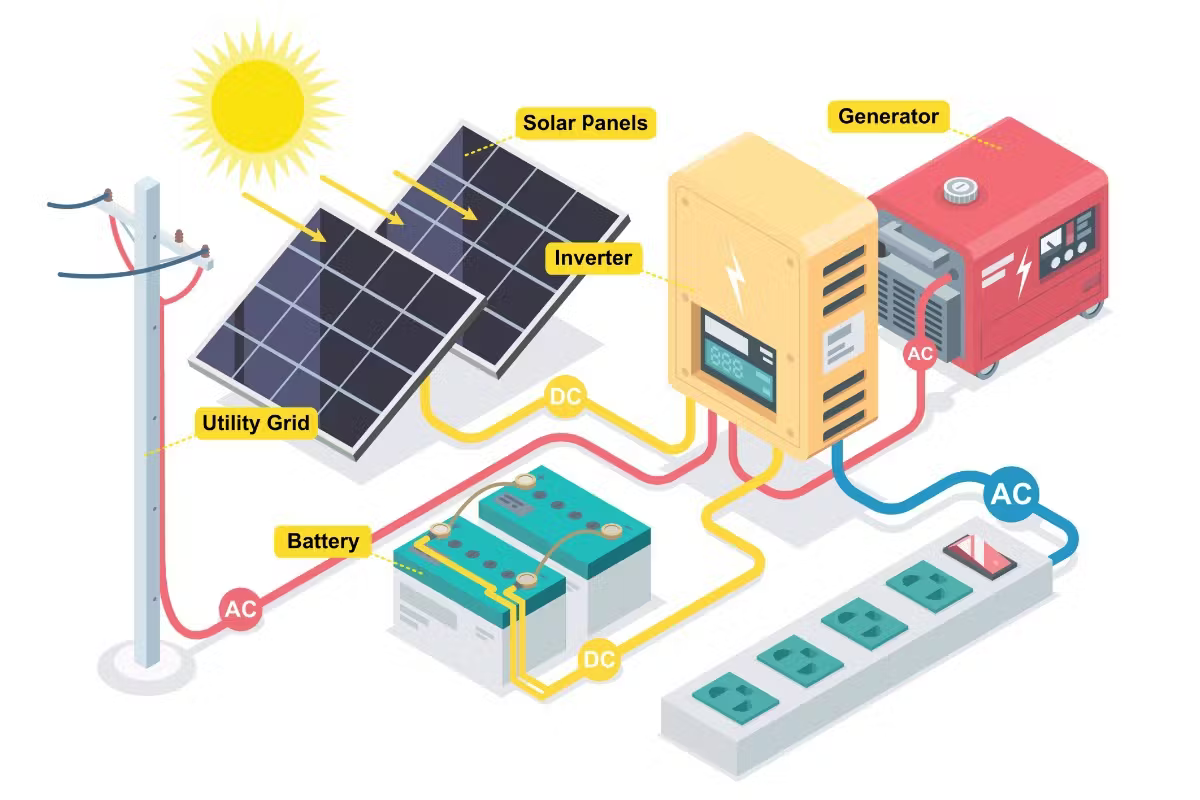
Hybrid Inverters
Hybrid inverters, on the other hand, go beyond the usual tasks of a solar inverter. Hybrid inverters convert direct current (DC) electricity to alternating current (AC) electricity and incorporate power backups such as batteries. This function enables hybrid inverters to supply backup power during power outages while also optimizing power consumption.
Hybrid inverters are a key advancement in renewable energy systems and a game changer in the use of solar energy. Hybrid inverters not only convert direct current (DC) power from solar panels into usable alternating current (AC), but also have the ability to store energy, making them adaptable and efficient options for household and commercial applications. Let’s take a closer look:
Integration of energy storage:
The ability to connect energy storage solutions such as batteries is the most important feature that distinguishes hybrid inverters from regular solar inverters. Solar panels gather, store, and use extra energy, resulting in a self-sufficient and dependable source of power. The flow of electricity between the solar modules, the batteries, and the power grid is controlled by hybrid inverters, which optimizes energy utilization and ensures an uninterrupted power supply.
Power backup during grid outages:
The ability of hybrid inverters to supply backup power during grid outages is one of their most significant advantages. When energy storage systems are installed, hybrid inverters can easily convert to battery power to keep essential equipment and systems operational during power outages. As a result, hybrid inverters are an appealing option for places where public power is unreliable.
Energy consumption has been reduced:
Intelligent energy management is enabled by hybrid inverters, allowing customers to optimize their energy consumption. Extra solar energy created throughout the day can be stored in batteries and used later, especially during periods of low solar radiation or high energy demand.This reduces reliance on the power grid and lowers energy expenses, making hybrid inverters a financially viable long-term choice.
Peak load management and tariffs based on time of use:
Programmable hybrid inverters control peak loads efficiently, minimizing reliance on grid power during peak demand periods and lowering energy expenditures. They store excess solar electricity during off-peak hours and use it during peak hours, strategically controlling energy usage in regions with time-of-use tariffs to benefit from lower electricity rates at specified times.
Scalability and adaptability:
Hybrid inverters are scalable and adaptable solutions. They are simple to incorporate into new installations or current solar systems.
Furthermore, the energy storage system’s capacity can be increased as needed to meet changing energy demands. Because of their scalability and versatility, hybrid inverters are suited for a wide range of applications, from houses to commercial buildings to off-grid installations.
In conclusion, hybrid inverters represent a critical tipping point in renewable energy systems. Integrating energy storage capacity into solar inverters allows for new levels of usability, dependability, and grid independence. Hybrid inverters provide a more comprehensive and adaptable solution for harvesting solar energy and transitioning to a more sustainable future, with backup power during grid disruptions, optimized energy use, and scalability.
Major differences between Solar Inverters and Hybrid Inverters

Are you ready to harness the sun’s power? Contact Us immediately for experienced guidance and installation of custom-tailored solar inverters or hybrid inverters. Begin your journey to energy independence and sustainability right now!